In various industries, plastics are positioning themselves as a versatile and innovative alternative to metal. This significant transition is fueled by a combination of factors, including technological advances in plastics processing, growing demands for durability and clear economic advantages. In this article, we explore how polymers and their characteristics are now positioning themselves as a preferred substitute for metal in a variety of applications.
Versatility in plastics processing:
Plastics processing, or the art of transforming plastics into useful products, offers an infinite range of possibilities in terms of design and functionality. Plastic materials such as polypropylene (PP), polyamide (PA), polycarbonate (PC) and many others are now manufactured with specific properties that rival those of metal. These materials can be molded, extruded or injected to create a variety of parts and products to meet the most demanding needs with great freedom of design.
One of the leading materials in this revolution is PPS, or Phenylene Polysulfide. This high-performance compound, often overlooked by the general public, is transforming the way we design and use parts in various industries, by advantageously replacing metal. Below are the reasons why PPS has become a preferred choice in the world of plastics processing.
What is PPS and why is it so special?
PPS is a high-performance thermoplastic polymer renowned for its exceptional chemical resistance, dimensional stability, high-temperature resistance and excellent electrical insulation. These properties make it ideal for demanding industrial applications, particularly where metal has traditionally been used.
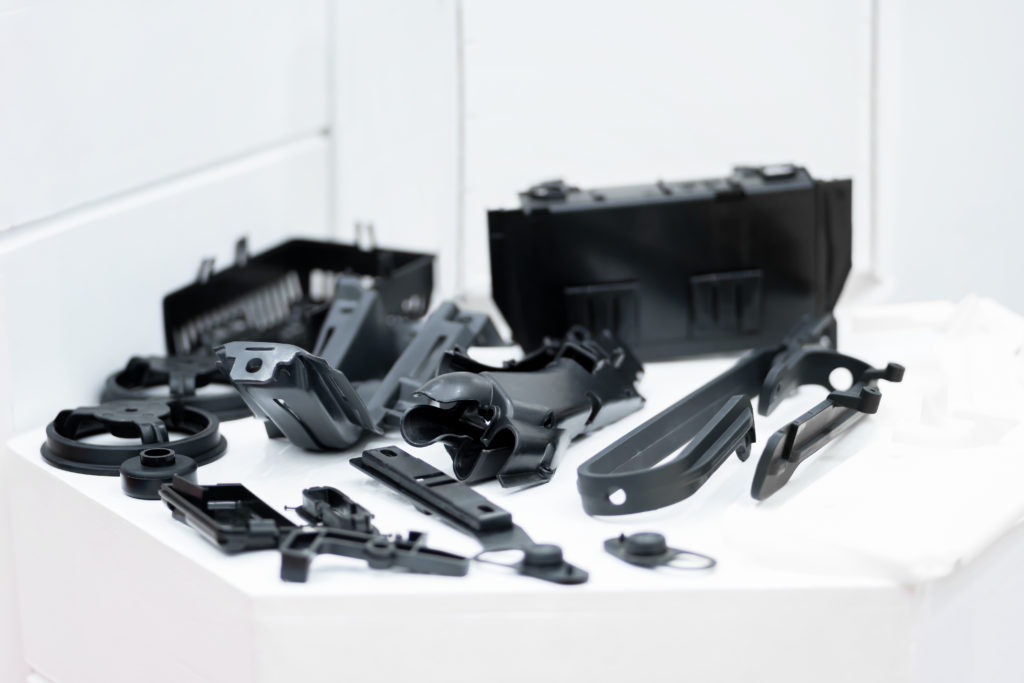


Why replace metal with PPS?
- Lightweight: PPS is much lighter than metal, reducing the overall weight of parts and equipment, which can lead to significant savings in transport and energy costs.
- Corrosion resistance: Unlike metal, PPS is corrosion-resistant, making it ideal for aggressive environments or applications exposed to corrosive chemicals.
- Thermal resistance: PPS can withstand extreme temperatures, making it an ideal choice for applications subject to high heat conditions, such as automotive components, electrical and electronic equipment, and even in the aerospace industry.
- Ease of manufacture: PPS can be injection-molded with precision, enabling the manufacture of complex parts to exacting tolerances. What’s more, it can be easily machined, welded and assembled, offering great flexibility in part design and manufacture.
- Durability: PPS is extremely durable and wear-resistant, giving it a long operational life. This translates into lower long-term maintenance and replacement costs. What’s more, this plastic can be recycled at the end of its life, helping to reduce its carbon footprint (an essential component in product life-cycle analysis – LCA).
Common applications of plastic in place of metal :
- Automotive: Plastics are widely used in the manufacture of automotive parts such as bumpers, body panels, seats, interiors, under-bonnet parts, etc., to reduce weight and improve fuel efficiency.
- Electronics: Electronic housings, connectors and other components are often made of plastic for its lightness and ability to insulate electrically.
- Construction: Plastic materials are used in a variety of construction applications, such as pipes and fluid transport, windows, doors, insulation, coatings, etc., offering performance equivalent or even superior to metal.



Leave a Reply